One of the most frequently mentioned terms when preparing for U.S. college admissions is GPA (Grade Point Average).
A lot of people feel lost at first because the grading systems in the U.S. and Korea are quite different.
But don’t worry—today, we’ll clearly break down how GPA is calculated and how the U.S. high school grading system works.
.
.
🎓 What Is GPA?
GPA (Grade Point Average) is a numerical indicator representing the average grade a student earns across all completed courses.
Most U.S. high schools and universities use a 4.0 scale.

.
.
🧮 How Is GPA Calculated?
GPA Formula
GPA = (Sum of each course’s grade points × credits) ÷ Total credits completed
GPA is calculated by multiplying each course’s grade point by its credit value, adding these together, and then dividing by the total number of credits. This means GPA is not just a simple average; each course’s weight (credits) influences the final score.
For example, let’s say a student took the four courses shown below:
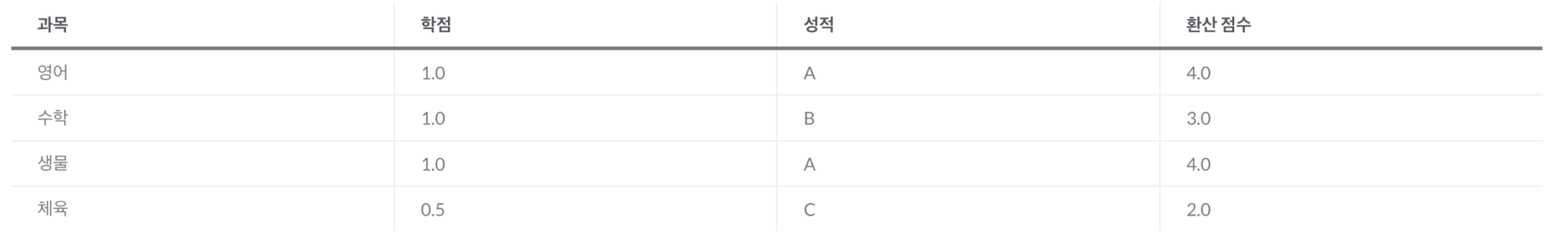
The calculation would be:
👉 (4.0 × 1.0) + (3.0 × 1.0) + (4.0 × 1.0) + (2.0 × 0.5) = 4.0 + 3.0 + 4.0 + 1.0 = 12.0
Total credits = 1.0 + 1.0 + 1.0 + 0.5 = 3.5
GPA = 12.0 ÷ 3.5 = 3.43
So this student’s GPA is 3.43.
Because GPA reflects course credit weight, it becomes a crucial metric in college admissions.
.
.
🌟 Weighted GPA vs. Unweighted GPA
In U.S. high schools, some courses may carry extra weight, and some may not.
The two systems used are:
- Unweighted GPA: All courses are treated equally (maximum 4.0)
- Weighted GPA: AP, IB, and Honors courses carry extra weight (maximum can exceed 5.0)
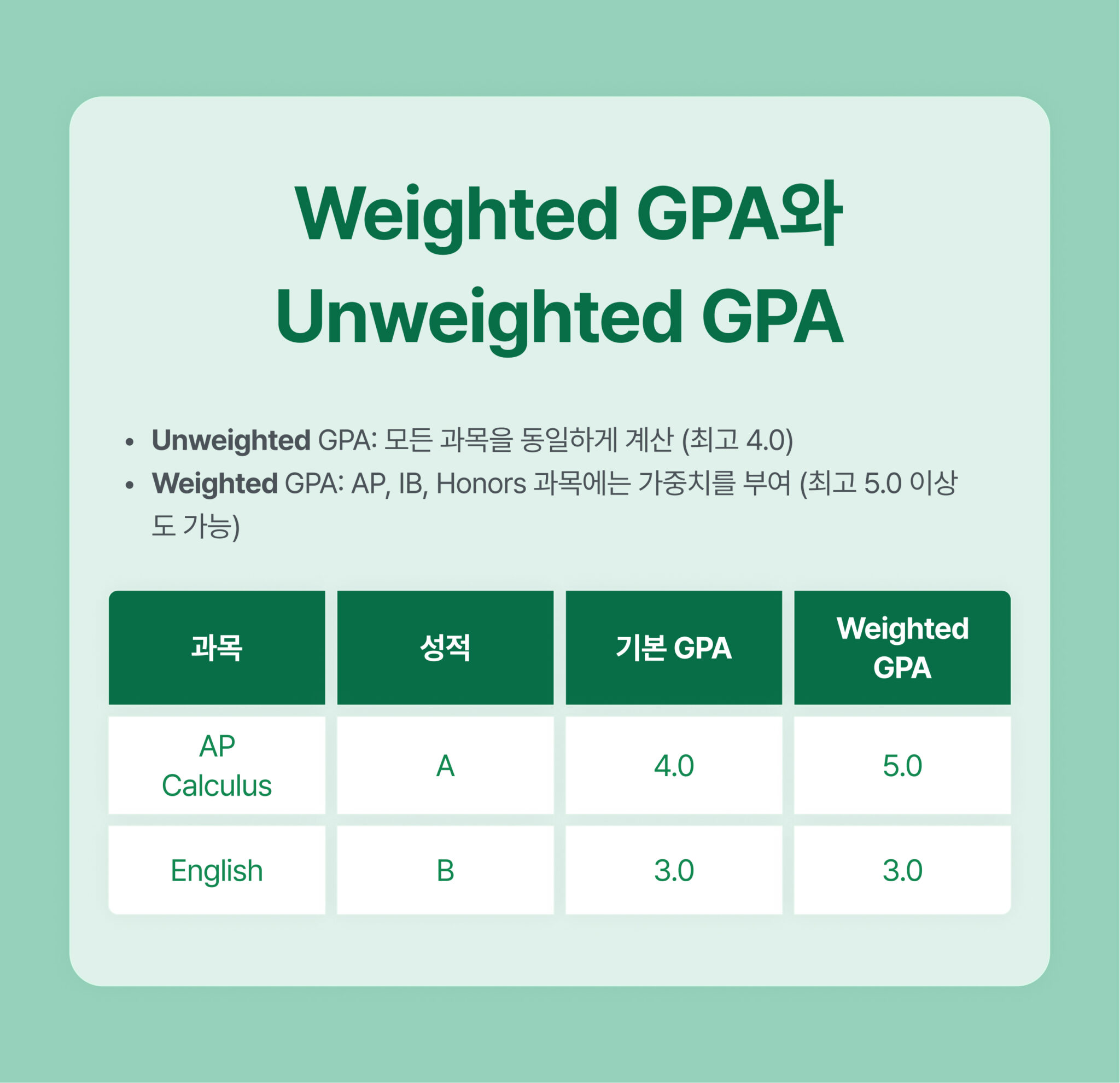
Example:
- A student who receives an A in AP Calculus → Unweighted GPA: 4.0 Weighted GPA: 5.0
- A student who receives a B in a regular English class → Unweighted GPA: 3.0 Weighted GPA: 3.0 (no extra weight)
As such, students who take challenging courses (AP, IB, Honors) and maintain high grades benefit from a higher Weighted GPA.
Since top universities also place strong emphasis on Weighted GPA, students should aim to take the most rigorous courses they can handle while maintaining a strong GPA.
.
.
📌 Other Important Academic Indicators
- Class Rank: Student ranking within the class/grade based on GPA
- Transcript: The official academic record submitted to colleges; includes courses, credits, GPA, etc.
- Course Rigor: Colleges value not just a high GPA but a challenging course load
.
.
🏫 When Does GPA Start to Matter?
Most U.S. students enter high school in 9th grade, and GPA is calculated across all four years (9–12th).
10th grade is when GPA begins to have a major impact on college admissions.
- The key is to take AP/IB courses while maintaining a strong GPA
- Increase course difficulty as you progress to strengthen your Course Rigor
- Beyond GPA, extracurriculars, volunteer work, and leadership activities play a major role in admissions
Now the U.S. GPA system should feel much clearer!
We’ll continue to cover U.S. academic and admissions topics in future posts.
If you have questions about GPA calculations or U.S. education, feel free to reach out to Loaning.ai anytime.
.
.
🔗 Popular Previous Post
👉 Complete Guide to AP/IB Programs in U.S. High Schools
Learn how advanced coursework can strengthen your path to college admissions.






